What is the difference between bio-passive and passive house ?
In fact, bio-passive house is the improved passive house, but built exclusively from environment friendly and recyclable materials, for example wood, sheep wool, straw, clay, etc.
Bio-passive house need not to use a forced venting, as it is in the case of a passive house, but it uses the natural venting provided by by using the suitable natural materials.
Bio-passive house may be designed in such a way it would be fully self-contained and independent. It maximally uses the renewable raw material sources and the natural energy sources (the Sun, water, wind, air).
What is the passive house ?
The term "passive house" has not been confirmed in our standards or legislation yet, therefore
Institute for energy passive houses - IEP comes from generally recognized definitions of Darmstadt Passivhaus-Institut (PHI).
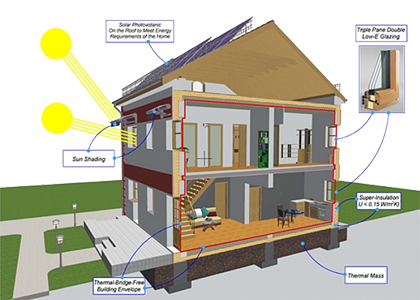 Passive house is an object that does not need the conventional heating or air-conditioning system for the provision of thermal comfort (either in winter or summer). So that this could be achieved, such a house should have the need for heat for heating reduced by 90% when compared with a common house.
Passive house is an object that does not need the conventional heating or air-conditioning system for the provision of thermal comfort (either in winter or summer). So that this could be achieved, such a house should have the need for heat for heating reduced by 90% when compared with a common house.
Such a specific heat rate (SHR - in kWh per m2 of utility area per year) is around 100 Wh/m2a in a common modern house, 250 Wh/m2a in average in an old prefab house, bellow 50 Wh/m2a in low-energy house, below 15 Wh/m2a in a passive house and approximately zero in the "zero" house.
SHR below 15 Wh/m2a is the basic characteristic of a passive house and it is demonstrated by calculation using the specialised software application (e.g. PHPP, for the preliminary calculation of PHVP available also in Slovak version at IEPD web) or using a computer simulation. In addition to the building perimeter surface parameters, its leakage test (blower-door test - BDT) is an important input data for calculations, its result should be bellow 0.6 for passive house and this value is applied when the house is not completed yet.
In addition to heating, the house needs energy also for water heating and for the operation of electric appliances. It is obtained from various sources, therefore we use the primary energy need for the expression of the efficiency of the total energy demands of a house – it should not exceed 120 kWh/m²a for a passive house. The confirmation of the calculated values is comprised in the certificate of the passive house from PHI (and the report from PHPP software application). A successful BDT is a precondition for the completed object - the house could not be legitimately called the passive house without passing the test.
These are the passive house criteria. Its characteristics describe the quality of peripheral shell and the structural design - there are not unambiguously defined values and conditions since they regard also the size of the object and its architectonic design, we often state them as well. U (or k) of opaque peripheral structures should be below 0.15 W/m²K (for smaller object it should often be around 0.1), U of windows should be below 0.8 W/m²K and as long as we want to consider the passive use of solar energy, they should transmit at least half of its energy ( g>0.5 ) The structure should be designed without significant heat leaks and with controlled venting with heat recovery from venting air. Solar collectors or the use of thermal pump can significantly contribute to the reduction of primary energy consumption. When as much materials made of formaldehyde-free renewable sources for the "production" and processing of which the least CO2 quantity is consumed as possible is used for the construction of such an object meeting the passive house standard, a man can live healthier, longer and cheaper. We can see the parameters of the passive house are exact (calculable and measurable) values - when someone offers a passive house, he/she/it should be able to prove meeting its criteria (or even to guarantee it). When someone writes about it, he/she/it should state the values (to the extent according to the level of publication expertise, however at least SHR should be calculated and specified). We should master the criteria and respect them - only this way we can prevent the degradation of the term "passive house" to an empty catchword accepted with mistrust.
Criteria for the passive house:
- The need of heat for heating per year is max. 15 kWh/m2
- The consumption of primary energy per year is max. 120 kWh/m2
- Specific caloric loss is max. 10 W/m2
- Air-tightness value of n50 is max. 0.6 h-1, the required airtightness of the house shall be verified by so called Bloower door test
- U-values of the perimeter shell are max. 0.10 - 0.15 W/m2K
 Passive house is an object that does not need the conventional heating or air-conditioning system for the provision of thermal comfort (either in winter or summer). So that this could be achieved, such a house should have the need for heat for heating reduced by 90% when compared with a common house.
Passive house is an object that does not need the conventional heating or air-conditioning system for the provision of thermal comfort (either in winter or summer). So that this could be achieved, such a house should have the need for heat for heating reduced by 90% when compared with a common house.